Nicole Bando | Dietitian & Lactation Consultant
Search by typing & pressing enter
Search by typing & pressing enter
Search by typing & pressing enter
Nutrition and Breastfeeding Articles

‘It is hard to know what to believe with so much conflicting nutrition
information. I provide you with the latest evidence-based facts.’
Categories


By Emma McShane & Nicole Bando
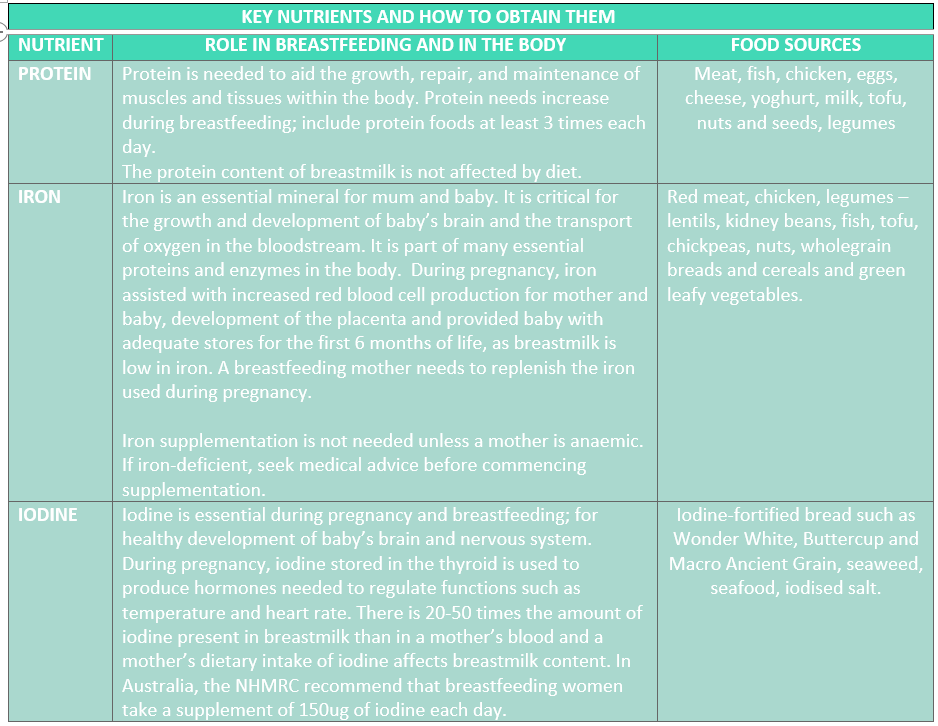
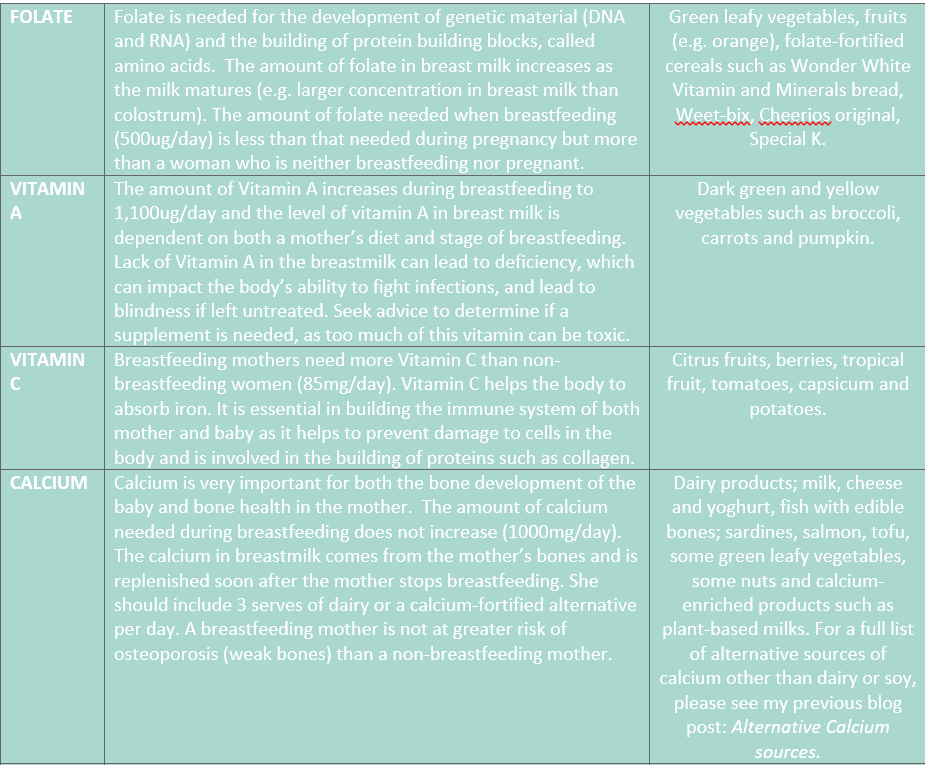
Nutrition whilst breastfeeding is vital to optimise the health of both mother and baby. New motherhood is a very busy time, and many women put their own health last. A woman’s remarkable body will produce the live, biodynamic, complete food that is breastmilk that evolves with her baby’s growing needs. Milk production is robust and will only be affected in very extreme circumstances. The average woman produces 750mls of breastmilk per day, from 1-6 months. Fat stores accumulated during pregnancy are used to fuel milk production when baby arrives, though this does not cover all of the energy needed to produce breastmilk. Some elements of breastmilk are impacted by a woman’s diet and those that follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, are at greater risk of vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
DID YOU KNOW?
- Adequate nutrition can help with coping with a new baby and the adjustment to motherhood, mood, and energy levels. Restrictive eating during breastfeeding can impact mood, milk supply, overall coping, and bone health.
- Certain nutrients in breastmilk, such as lactose and protein are fairly constant, however the fat content of breastmilk changes according to how empty the breast is. The types of fatty acids and quantities of iodine and Vitamin B12 are also affected by the mother’s diet.
- A mother’s varied diet exposes baby to different flavours and tastes, which will help baby to accept a wider range of solid foods, including fruit and vegetables.
- Regular nutritious meals and snacks are important to nourish both mother, and baby. There is no need to aim for dietary perfection.
ENERGY:
An extra 2000kJ per day is needed for a breastfeeding mother, though this can change depending on individual needs. This is equivalent to a serving of spaghetti Bolognese with cheese (1 cup pasta and ½ cup sauce), or a bowl of porridge with apple, yoghurt, and nuts (½ cup uncooked oats, made with 1 cup of milk, 1 apple and a handful of nuts) or a combination of snacks throughout the day, such as yoghurt (¾ cup), popcorn (small packet/1 cup), crumpets, and peanut butter (1 crumpet with 1 tb of nut butter). Studies show that not eating enough can directly impact milk supply and composition, so a wholesome diet is vital to fuel both mother and baby.
FLUID:
Breastmilk production requires fluid, so a breastfeeding woman requires more fluid than usual. The amount depends on various factors such as weather conditions, activity levels, and the food eaten. Be guided by your body, and ensure you’re drinking water consistently throughout the day.
CAFFEINE:
Caffeine transfers directly into breastmilk, so avoid large quantities of caffeinated drinks when breastfeeding. 1% of caffeine enters breastmilk and peaks an hour after consumption. A newborn baby can take up to 160 hours to process caffeine, however by 6 months that drops to 2-3 hours, so an older baby is able to better tolerate caffeine. A morning latte or a few cups of tea across the day might not cause any issue, but observe baby; a mother may consider changing to a decaffeinated tea or coffee if she notices that her baby is very wakeful after her morning coffee. A moderate amount of caffeine a day, such as two cups of coffee (latte or espresso), three cups of instant coffee or four cups of tea is usually fine. Remember that sources of caffeine include: cola, chocolate, tea, guarana, and energy drinks.
Caffeine can also affect the let-down (the milk ejection reflex) and worsen nipple vasospasm (occurs when blood vessels tighten and spasm, causing nipple pain).
ALCOHOL:
The safest option while pregnant and breastfeeding is to avoid alcohol altogether, as it can reduce breastmilk production and impact baby’s growth and development. Alcohol is present in breastmilk in the same levels as the bloodstream and it takes approximately 2-3 hours for the mother’s body to clear the alcohol in one standard drink. This time increases with each drink consumed. So if choosing to consume alcohol, wait around 2 hours before breastfeeding. Any milk expressed before the 2-hour window will need to be discarded, as it is not safe for the baby to consume. If there are times where a mother plans on drinking more than one standard alcoholic drink, plan ahead and express some breast milk beforehand to feed baby during this time. Below are two links to resources for further information:
MIXED FEEDING:
Any amount of breastfeeding increases a woman’s dietary requirements, however given the wide variation in breast milk production when mixed feeding, it can be difficult to estimate. A woman should use her appetite as a guide and may require additional foods from the core groups. A dietitian can help to guide this.
DO CERTAIN FOODS INCREASE BREASTMILK PRODUCTION?
Oats: Many women wonder if oats or lactation cookies help with milk supply, however, there is no clear evidence to support this.
Fenugreek: There is poor quality and limited evidence to suggest that fenugreek increases milk supply.
Breastfeeding with good attachment, flexibly and frequently is the best way to protect milk supply.